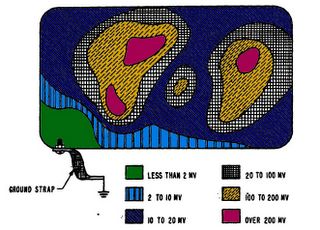
PWB Ground Potential Graph
This is a graph showing how the ground potential varies as it moves from a single point ground connection. A single point ground connection eliminates potential ground loops. How ever; a single point ground connection also does not provide a good ground potential to all points of the circuit board.
Ground loops cause unintended currents to flow in connections which should have zero current flow. Unintended current flowing in a circuit is called noise, because that current flow was not designed into the circuits operation. Avoid Ground loops or multiple circuit to ground connections in your design.
Many circuits can tolerate the rise or difference in ground potential depicted in the picture. Locate analog devices near the ground strap, and push digital devices away. An Analog IC may require a near perfect reference, while digital devices will tolerate a much larger change in the ground potential. For additional reference data of Printed Circuit Boards, check out PCB Terms and Definitions.
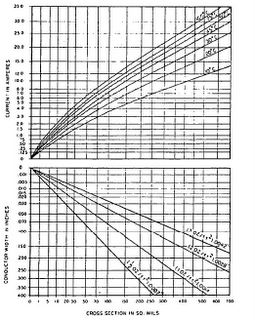
PWB Information